
特殊染剂 – 哪一个、如何使用以及为什么? 第 II 部分:结缔组织

结缔组织 - 简介
结缔组织提供连接并结合细胞和器官的基质,从而支撑身体。体内有三种类型的结缔组织。
胶原是一种强蛋白,它是韧带和肌腱的主要组分。它还负责皮肤弹性,是可以通过 H&E 观察的最明显的类型。

弹性纤维位于皮肤和血管壁内。它们由弹性蛋白(一种有柔性,并可让身体中的许多组织在拉伸或收缩后恢复原形的蛋白)组成,并且无法通过 H&E 显示。
网状纤维由胶原组成,在神经纤维、脂肪细胞、淋巴结以及平滑肌和骨骼肌纤维周围形成一个脆弱的框架。它们无法通过 H&E 显示。
显示结缔组织的最常用染剂
三色染色 - Masson
使用三种染料进行选择性染色,包括肌肉(红色)、胶原纤维(蓝色)、红细胞(红色)和胞核(黑色)。
这些染料用于肝活检染色,以确定肝硬化的纤维化程度,还用于肾活检染色,以突出基底膜,显示免疫沉积物。这些染料还用于区分肿瘤细胞中的平滑肌和胶原,并确认胶原是否增加。
过程

结果
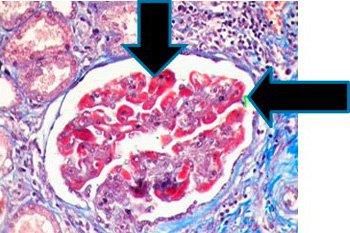
实验步骤 – 孵育时间可能因制造商的指南而异
| 1. | 将玻片放入水中 | |
| 2. | 在 Bouin(作为一种使染料结合组织的媒染剂)中孵育。 | |
|
通常过夜 | |
|
10-15 分钟 | |
| 注:如果在微波炉中加热 Bouin,切勿在溶液中加热玻片;加热 Bouin,从微波炉中取出,将玻片放入玻片染色缸,盖上盖子,并在微波炉外孵育。 | ||
| 3. | 用流水冲洗干净,去除所有 Bouin 痕迹 | |
| 4. | Weigert 苏木精 | 5-10 分钟 |
| 5. | 用流水冲洗 | 5 分钟 |
| 6. | 比布列希猩红 | 15 分钟 |
| 7. | 用流水冲洗 | |
| 8. | 磷钨/磷钼酸 | 15 分钟 |
| 9. | 直接用苯胺蓝(不冲洗) | 5 分钟 |
| 10. | 直接用 1% 冰醋酸 | 1-3 分钟 |
| 11. | 用流水冲洗 | |
| 12. | 脱水、清除和封片 |
三色染色疑难排除:
必须使用优质 Bouin,使用的温度适当,孵育时间适当。使用胶原磷钨-磷钼酸完成区分,直到去除所有红色。如果肌肉呈淡红色,则检查 Bouin 和/或比布列希猩红的活性。如果胶原太淡,则缩短在 1% GLAA 中的孵育时间。胞核 - 黑色
一步三色染色 - Gomori
一种溶液完成全部染色:肌肉、胶原纤维、纤维蛋白和红细胞。有两种配方:蓝色—适用于选择像 Masson 中一样的胶原蓝色的情况、绿色—适用于选择胶原绿色的情况,所有其他结果均与 Masson 相似。
过程

结果


实验步骤
孵育时间可能因制造商指南而异。
| 1. | 将玻片放入水中 | |
| 2. | 在 Bouin(作为一种使染料结合组织的媒染剂)中孵育。 | |
|
通常过夜 | |
|
10-15 分钟 | |
| 注:如果在微波炉中加热 Bouin,切勿在溶液中加热玻片;加热 Bouin,从微波炉中取出,将玻片放入玻片染色缸,盖上盖子,并孵育 | ||
| 3. | 用流水冲洗干净,去除所有 Bouin 痕迹 | |
| 4. | Weigert 苏木精 | 5-10 分钟 |
| 5. | 用流水冲洗 | 5 分钟 |
| 6. | 一步蓝色/绿色溶液 | 15 分钟 |
| 7. | 直接用 1% 冰醋酸 | 1 分钟 |
| 8. | 用流水冲洗 | |
| 9. | 脱水、清除和封片 |
Verhoeff van Gieson 弹性纤维染剂
Verhoeff van Gieson 弹性纤维染剂用于识别弹性组织萎缩(如肺气肿)、血管疾病(动脉硬化)证据以及肿瘤侵袭血管情况。
过程

结果

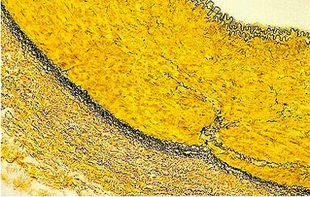
实验步骤
孵育时间可能因制造商指南而异。
| 1. | 将玻片放入水中 | |
| 2. | Verhoeff 弹性纤维染剂 – 工作溶液(根据制造商) | 15 分钟 |
| 3. | 用流水冲洗干净 | |
| 4. | 用 2% 氯化铁区分 | 1-2 分钟 |
| 5. | 用流水冲洗 | 5-10 分钟 |
| 6. | 5% 硫代硫酸钠 | 1 分钟 |
| 7. | 用流水冲洗 | |
| 8. | 用 van Gieson 溶液复染 | 30 秒钟 - 1 分钟 |
| 9. | 跳过 95%,并用 100 x 2 快速脱水 | |
| 10. | 清除并封片 |
弹性纤维染剂疑难排解:
由于会快速氧化,Verhoeff 溶液需要在每次使用时新鲜制备。不要用氯化铁过度区分,因为染料分子很喜欢这种物质(就像喜欢与其结合的组织分子一样),且将很容易与组织分离,您必须从零开始。 孵育几秒钟,然后快速冲洗,并用显微镜观察是否存在弹性组织纤维。当它们是黑色且易于与胶原和其他组织类型区分时,停止这个过程。
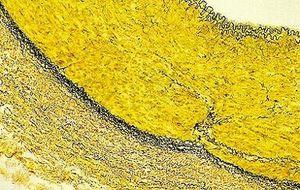
同样,不要在 van Gieson 中孵育过长时间,因为溶液中的苦味酸将继续区分结合的苏木精。
Gomori 网状纤维
网状纤维支撑身体,在肝、脾和肾中常见。特有的网状蛋白模式可以帮助诊断肝硬化、骨髓早期纤维化、肿瘤(包括血管肉瘤-血管壁细胞肿瘤、纤维母细胞瘤和横纹肌肉瘤-附着于骨骼的肌肉肿瘤)。它们还可以帮助诊断上皮和非上皮肿瘤。
网状蛋白染剂使用银,并依赖于纤维的嗜银特性。嗜银细胞可吸附银,但不能减少银。吸附 = 基于表面的过程,而吸收 = 渗透组织。嗜银细胞需要一种还原剂/显影剂将不可见的银盐转化为可见的金属银。
过程

结果

实验步骤
| 1. | 将玻片放入水中 | |
| 2. | 用高锰酸钾氧化 | 10 分钟 |
| 3. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 3 分钟 |
| 4. | 草酸 | 1 分钟 |
| 5. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 2 分钟 |
| 6. | 用硫酸铁铵敏化 | 15 分钟 |
| 7. | 用蒸馏水冲洗 | 2 分钟 |
| 8. | 用氨银浸透 | 2 分钟 |
| 9. | 用蒸馏水冲洗 | 1 分钟 |
| 10. | 用 20% 无缓冲福尔马林显影 | 1 分钟 |
| 11. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 2 分钟 |
| 12. | 用 0.1% 氯化金染色 | 3–5 分钟 |
| 13. | 用水冲洗 | 1 分钟 |
| 14. | 5% 硫代硫酸钠 | 1 分钟 |
| 15. | 用水冲洗 | 1 分钟 |
| 16. | 用核固红复染 | 3-5 分钟 |
| 17. | 用水稍微冲洗 | 15 秒种 |
| 18. | 脱水、清除和封片 |
Gomori 网状蛋白疑难排解:
应用蒸馏水和洁净的玻璃器皿(无需去除酸)新鲜制备银溶液。请小心制备银溶液。使用较旧无氨氢氧化铵会导致溶液失效。请勿使用过量的氢氧化铵清除银/氢氧化钠溶液。过量的氢氧化铵会导致染色较浅。
如何制备氨银:

如何使用一个流程显示胶原、弹性纤维、网状纤维、胞核和肌肉
Movat Pentachrome
Movat Pentachrome 是一种超级结缔组织染剂。它可以用来研究心脏组织、血管、血管病和肺病。由于可以很好地区分胶原、弹性纤维、纤维蛋白和肌纤维,Movat 可以揭示常规和正常特殊染剂无法显示的细微变化。
过程

结果

实验步骤
孵育时间和试剂顺序可能因制造商而异,但结果相似。
| 1. | 将玻片放入水中 | |
| 2. | 阿尔新蓝 | 20 分钟 |
| 3. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 5 分钟 |
| 4. | 碱性酒精 | 60 分钟 |
| 5. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 10 分钟 |
| 6. | 用蒸馏水冲洗 | |
| 7. | Verhoeff 弹性纤维溶液 | 12 至 15 分钟 |
| 8. | 蒸馏水 x 2 | |
| 9. | 氯化铁 | 2 至 3 次浸涂 |
| 10. | 用蒸馏水冲洗 | |
| 11. | 硫代硫酸钠 | 1 分钟 |
| 12. | 用流水冲洗干净 | 5 分钟 |
| 13. | 藏花猩红 – 酸性品红 | 1:30 至 3 分钟 |
| 14. | 蒸馏水 x 2 | |
| 15. | 0.5% 醋酸水 | |
| 16. | 5% 磷钨酸水溶液 x 2 | 每次 5 分钟 |
| 17. | 0.5% 醋酸水 | |
| 18. | 无水酒精 x 3 | 快速浸涂 |
| 19. | Safran | 15 分钟 |
| 20. | 无水酒精 x 2 | |
| 21. | 清除并封片 |
Movat Pentachrome 疑难排解
阿尔新蓝的 PH 值应为 2.5. 完全去除碱性酒精对于良好的染色至关重要。Verhoeff 溶液应在每次使用时新鲜制备,因为它会很快氧化。切勿过度用氯化铁区分弹性纤维。浸涂一次或两次,然后用蒸馏水冲洗,再用显微镜检查。 必要时重复。不要使用分级的酒精脱水,但要用无水酒精开始。在染色过程中,切勿让切片干燥。
About the presenter

Carolyn Doan received her ASCP registration in 1969 after completing classes at Georgia State University and St Joseph school of Histotechnology in Atlanta, Georgia. For 40 years she shared her passion for histology in research (at Yerkes Primate Research Center), in the clinical world (managing the Pathology Department at Florida Hospital in Orlando and serving on the board of the Florida State Licensure Task Force and as president of the Florida State Society for Histotechnology), and in industry (as a Sales executive, Marketing Manager and North American staining sales specialist). Since her retirement in 2013, she founded Creative Histology Consulting.
References
参考书目
Geoffrey Rolls. “101 Steps to Better Histology – A Practical Guide to Good Histology Practice”. Pathology Leaders/Articles
Shaikh, Dr. Imran, “Special Stains in Histopathology.” Kem Hospital, 2012
Sheehan and Hrapchak, “Theory And Practice Of Histotechnology” Connective Tissue 2nd Edition 10: 180-200.
Culling, CFA, Allison R.T, Barr W.T., (1985) Cellular Pathology Technique, ed. 4. Butterworths, London, England.
Wikipedia – Ammoniacal Silver, Nov, 2013.
Russel, H.K.: A Modification of the Movat Pentachrome Stain. Arch Pathol, 94: 187, 1972
Leica Biosystems Knowledge Pathway content is subject to the Leica Biosystems website terms of use, available at: Legal Notice. The content, including webinars, training presentations and related materials is intended to provide general information regarding particular subjects of interest to health care professionals and is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, medical, regulatory or legal advice. The views and opinions expressed in any third-party content reflect the personal views and opinions of the speaker(s)/author(s) and do not necessarily represent or reflect the views or opinions of Leica Biosystems, its employees or agents. Any links contained in the content which provides access to third party resources or content is provided for convenience only.
For the use of any product, the applicable product documentation, including information guides, inserts and operation manuals should be consulted.
Copyright © 2025 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.