
Multiplexing In Tissue-Based Research: Chromogenic Staining and Automation

Immunohistochemistry ( IHC ) detects proteins of interest within whole tissue sections, keeping cellular organization intact. Evolving from conventional IHC (single slide, single marker), multiplex IHC is an advancement on this technique that enables the detection of multiple markers of interest simultaneously in one tissue section.
The ability to analyze multiple markers is important as cells do not exist or act in isolation, and cellular responses involve activation of several pathways that influences the nature of their responses.
Multiplexing can therefore be applied to address several types of research questions including, but not limited to, the spatial arrangement or quantity of different cell lineages, phenotyping of immune cells, evaluation of multiple effectors of signal transduction pathways, and the distribution of novel drugs.

Using single-plex, chromogenic IHC, they showed that the density of PD-L1+ cells correlated with a better response to immunotherapy, as did an increased density and spatial proximity of PD-1+ lymphocytes to PD-L1+ cells. Using a multiplex panel and the BOND RX stainer, Giraldo et al1 were able to determine that the PD-1+ cells consisted of several different immune cell types including CD8, CD4, Foxp3 T-cells, and some CD20 B-cells. Their findings suggest that multiple immune cell types may be involved in tumor regression of Merkel cell carcinoma, that could lead to uncovering important mechanisms involved in therapeutic responses. Overall, their study highlights that IHC is an important tool for cancer research. It also demonstrates that multiplex IHC can reveal important features of such a heterogenous and complex disease that can unveil potential mechanisms, biomarkers, as well as paving the way for further directed research.

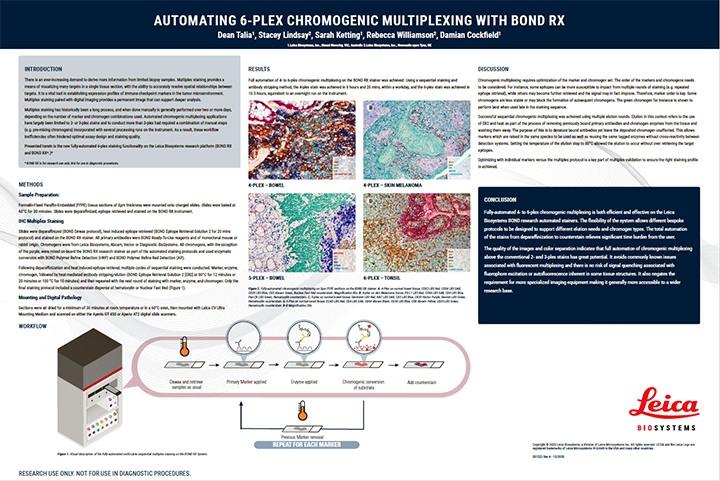
Although immunofluorescent multiplexing has been the most popular method of choice to date, chromogenic multiplexing with 3+ markers is becoming a more viable option as there are now more commercially available chromogens and color choices. This results in a permanent, multi-color slide that can be imaged and scanned with brightfield microscopes/scanners to generate a complex biological picture.
Performing IHC manually may spark dread due to the lengthy nature of the process, however Leica Biosystems offers a flexible, consistent, fully automated solution that decreases hands-on time for up to 6-plex chromogenic staining. Automation with the BOND RX stainer offers the following advantages for staining:

Download the poster to find out more about chromogenic multiplexing on the BOND RX fully automated stainer for up to 6-plex chromogenic staining.
발표자 소개

Rhian is a Scientist from Swansea University in Medical and Healthcare Studies and was featured in several collaborative publications. Rhian’s research-based background focused on tissue-based pathology in Multiple Sclerosis, primarily using immunohistochemical analysis and in vitro molecular techniques. She spent a short period conducting routine PCR testing for COVID-19 at the end of 2020.
참조 문헌
- Giraldo N A, Nguyen P, Engle E L, et al. Multidimensional, quantitative assessment of PD-1/PD-L1 expression in patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and association with response to pembrolizumab. J. Immunotherapy Cancer. 2018;6;99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0404-0
Related Content
Leica Biosystems 콘텐츠는 Leica Biosystems 웹사이트 이용 약관의 적용을 받으며, 이용 약관은 다음에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 법적고지. 라이카 바이오시스템즈 웨비나, 교육 프레젠테이션 및 관련 자료는 특별 주제 관련 일반 정보를 제공하지만 의료, 규정 또는 법률 상담으로 제공되지 않으며 해석되어서는 안 됩니다. 관점과 의견은 발표자/저자의 개인 관점과 의견이며 라이카 바이오시스템즈, 그 직원 또는 대행사의 관점이나 의견을 나타내거나 반영하지 않습니다. 제3자 자원 또는 콘텐츠에 대한 액세스를 제공하는 콘텐츠에 포함된 모든 링크는 오직 편의를 위해 제공됩니다.
모든 제품 사용에 다양한 제품 및 장치의 제품 정보 가이드, 부속 문서 및 작동 설명서를 참조해야 합니다.
Copyright © 2025 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.



