
HistoCore Spectra CV coverslipper reduces turnaround time by 47% from glass coverslipping to slide drying completion
During the demonstration using the HistoCore SPECTRA CV Coverslipper, the customer experienced:
Preface
In the current histopathology process, growing workloads are driving the need for standardization, increased productivity and to further reduce technologist hands-on time wherever automation is possible. Thus, this testimonial focuses on evaluating the entire coverslipping workflow, demonstrating that the use of the HistoCore SPECTRA CV Coverslipper built-in oven with active heating technology meets those needs.
Introduction
It is sometimes assumed that film coverslippers enable a faster slide processing time compared to glass coverslippers.
Slide processing time is commonly defined as the time needed for coverslipping only. However, in a real laboratory workflow, the slides need to be completely dry before any further handling.
Furthermore, dried slides are necessary to reduce exposure to hazardous fumes and are an absolute must when using digital pathology.
To meet the requirement of having completely dried slides there are three commonly practiced options:
- Use a coverslipper with a built-in oven
- Remove the slides from a coverslipper to dry in a fume hood (no heat applied) or external oven
- Leave the slides to dry in a coverslipper drying station (no heat applied)
Method
The purpose of this assessment was to evaluate and understand processing times of glass vs. tape coverslipped microscopic slides for diagnostic evaluation. The HistoCore SPECTRA CV Coverslipper (for glass coverslipping) and the Sakura Tissue Tek® Film Coverslipper were used for comparison. This trial was conducted at an independent university pathology laboratory.
The coverslipping and drying process was evaluated for a full load of 60 slides per coverslipper. 60 slides were selected for this trial since it is the maximum number of slides possible to include in one batch for both coverslippers. The process began with loading 60 slides onto each system and ended by the time the slides were completely dry.
Slide dryness was defined by the following factors:
- No xylene residue visible on the slides
- No xylene residue visible between the slides and the staining rack
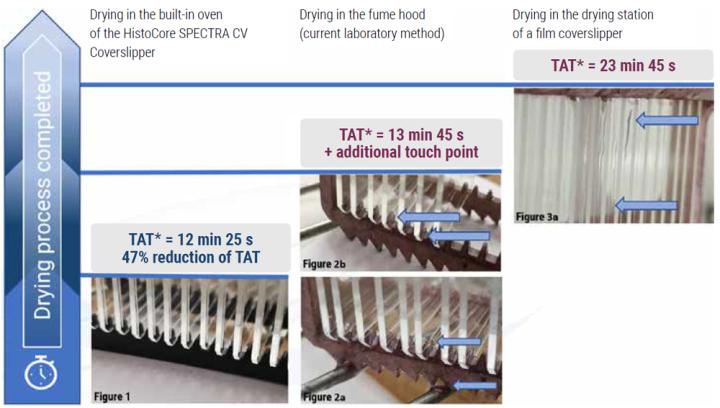
Results
Conclusion
In this assessment we have demonstrated the use of the HistoCore SPECTRA CV Coverslipper built-in oven with active heating technology to reduce TAT* by 47% compared to using the drying station of the existing film coverslipper. Additionally, the laboratory staff reported minimized exposure to xylene fumes due to the reduction of workflow steps and the efficient standardized drying methodology.
Furthermore, results showed a decrease in TAT* by 9.7% versus the commonly practiced workaround of removing the slides from the film coverslipper and placing them under an external fume hood for drying. Thereby the lab was also able to eliminate the additional step in the workflow of slide transportation from the film coverslipper to the fume hood.
*TAT= turnaround time from coverslipping until slide drying complete
Projections and Realized Results are specific to the institution where they were obtained and may not reflect the results achievable at other institutions.
Want to see how the HistoCore Spectra CV coverslipper can help improve your lab's turnaround time?
Leica Biosystems content is subject to the Leica Biosystems website terms of use, available at: Legal Notice. The content, including webinars, training presentations and related materials is intended to provide general information regarding particular subjects of interest to health care professionals and is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, medical, regulatory or legal advice. The views and opinions expressed in any third-party content reflect the personal views and opinions of the speaker(s)/author(s) and do not necessarily represent or reflect the views or opinions of Leica Biosystems, its employees or agents. Any links contained in the content which provides access to third party resources or content is provided for convenience only.
For the use of any product, the applicable product documentation, including information guides, inserts and operation manuals should be consulted.
Copyright © 2025 Leica Biosystems division of Leica Microsystems, Inc. and its Leica Biosystems affiliates. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica Logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH.